Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction: Is Influenza a Virus?
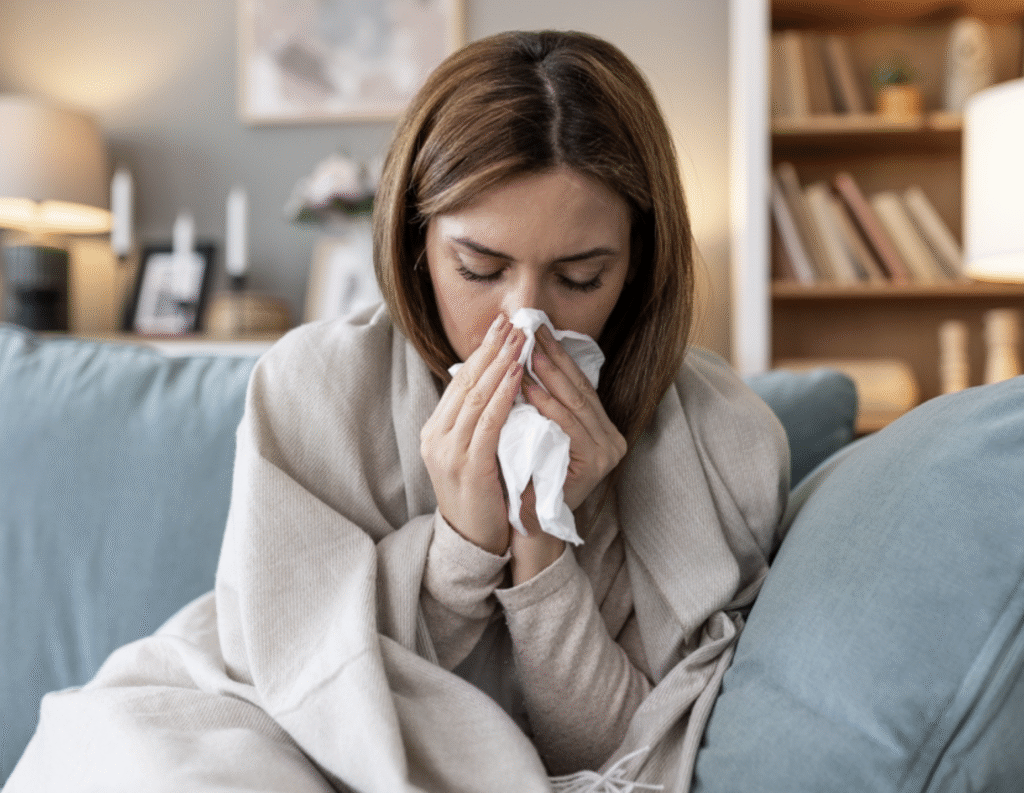
Yes—influenza is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses. Unlike bacteria, which are living organisms, viruses require a host to survive and reproduce. That’s why flu spreads quickly among people—once inside your body, the virus hijacks your respiratory cells to multiply. (CDC)
What Is Influenza?
Influenza (the flu) is an infection of the nose, throat, and sometimes lungs. It ranges from mild to severe and can even cause death in vulnerable groups. Seasonal flu epidemics occur annually, typically peaking in colder months. (CDC)
The Science Behind the Influenza Virus
-
Influenza viruses are divided into Types A, B, C, and D.
-
Types A and B cause the seasonal flu epidemics seen each year.
-
These viruses mutate often, which is why the flu vaccine is updated annually.
How the Flu Virus Spreads
-
Through respiratory droplets when people cough, sneeze, or talk.
-
By touching contaminated surfaces and then touching your face.
-
People can spread the flu before symptoms appear and remain contagious for days afterward. (CDC)
Incubation & Onset of Symptoms
-
Symptoms usually appear 1–4 days after exposure, with an average of 2 days.
-
The flu often starts suddenly—you may feel fine one day and very sick the next. (CDC)
Common Symptoms of Influenza
According to the CDC, flu symptoms include:
-
Fever or chills
-
Cough
-
Sore throat
-
Runny or stuffy nose
-
Muscle or body aches
-
Headaches
-
Fatigue (tiredness)
-
Vomiting and diarrhea (more common in children)
Is Influenza the Same as a Cold?
No. While both are viral respiratory infections, flu is more severe.
| Symptom | Cold | Flu |
|---|---|---|
| Onset | Gradual | Sudden |
| Fever | Rare | Common |
| Aches | Mild | Severe |
| Fatigue | Mild | Severe & prolonged |
| Sneezing | Common | Less common |
High-Risk Groups for Severe Flu
Some people are more likely to develop complications from Influenza:
-
Adults 65+
-
Children under 5, especially under 2
-
Pregnant women
-
People with chronic conditions (asthma, diabetes, heart disease)
-
People with weakened immune systems
Complications of Influenza
The flu virus can lead to serious health issues:
-
Pneumonia
-
Worsening of chronic conditions (e.g., asthma, heart disease)
-
Heart inflammation (myocarditis)
-
Brain inflammation (encephalitis)
-
Multi-organ failure in severe cases
Emergency Warning Signs
Seek medical help immediately if you notice these symptoms:
In Children:
-
Rapid or difficult breathing
-
Bluish lips or face
-
High fever (above 104°F) not improving with medicine
-
Seizures
In Adults:
-
Shortness of breath
-
Persistent chest pain
-
Confusion or difficulty waking up
-
Severe dizziness
-
Worsening of chronic illnesses
How to Prevent the Flu Virus
-
Get vaccinated annually—the best defense.
-
Wash hands often with soap and water.
-
Avoid close contact with sick people.
-
Cover coughs and sneezes.
-
Clean commonly touched surfaces.
Treatment Options: What Works?
-
Rest and hydration.
-
Over-the-counter medicines for fever and aches.
-
Antiviral drugs (if prescribed) can shorten illness if started early.
FAQs
Q: Is influenza always caused by a virus?
Yes, influenza is exclusively viral—not bacterial.
Q: Can antibiotics treat the flu?
No. Antibiotics work on bacteria, not viruses.
Q: How long does the flu last?
Typically 3–7 days, but cough and fatigue may last longer.
Q: Can you get the flu more than once?
Yes, because different strains circulate and the virus mutates.
Q: Is the flu vaccine 100% effective?
No, but it significantly reduces risk of severe illness and hospitalization.
Q: Can influenza lead to death?
Yes, particularly in high-risk groups, which is why prevention is crucial.
Conclusion
So, is influenza a virus? Absolutely. It’s a highly contagious viral infection that can range from mild to deadly. The best defense is prevention through vaccination, hygiene, and early treatment when necessary. Understanding the flu virus helps protect not just yourself, but also your community.
Read more about Respiratory diseases: COPD.
PharmD with expertise in pharmaceuticals and a passion for making medical knowledge clear, accurate and accessible to all