Understanding COPD Causes: A Comprehensive Guide to Lung Health
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung condition that obstructs airflow, often making everyday tasks increasingly difficult. With
COPD causes ranging from smoking to environmental exposure, understanding this condition can empower individuals to take proactive steps in prevention and management.
What Causes COPD?
COPD is primarily linked to prolonged exposure to lung irritants that damage the airways and lung tissue over time. Below are the major contributors:
1. Smoking: The Primary Culprit
Smoking is responsible for the majority of COPD cases. Tobacco smoke damages the airways, reducing lung capacity and triggering chronic inflammation.
2. Secondhand Smoke Exposure
Even non-smokers are at risk if they frequently inhale secondhand smoke, which carries harmful chemicals that irritate lung tissues.
3. Occupational Hazards
Workers exposed to dust, fumes, and chemicals in industries such as mining, manufacturing, or agriculture are at heightened risk of COPD.
4. Air Pollution
Urban residents and those in heavily industrialized areas may develop COPD due to prolonged exposure to pollutants and fine particulate matter in the air.
5. Genetic Predisposition
A rare condition known as Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency can lead to COPD, even in non-smokers, by reducing the lungs’ ability to repair damage.
6. Respiratory Infections
Severe or recurrent respiratory infections in childhood may impair lung development, increasing vulnerability to COPD in later life.
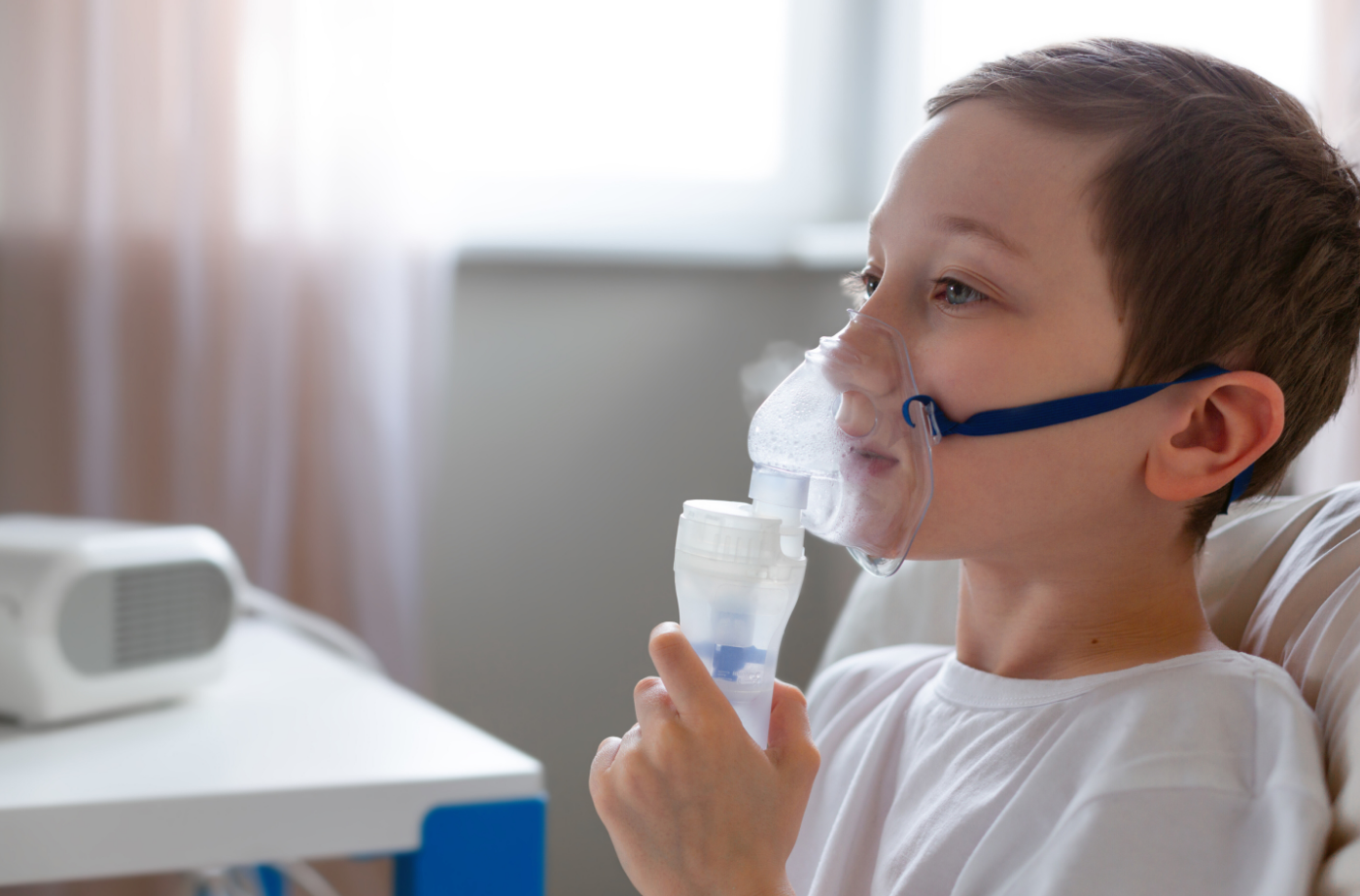
Recognizing the Symptoms of COPD
Early detection of COPD symptoms can improve outcomes and quality of life. Here’s what to watch for:
- Shortness of Breath: Initially noticeable during exercise, progressing to difficulty even at rest.
- Chronic Cough: Persistent coughing, often accompanied by mucus production.
- Wheezing: A whistling sound during breathing due to restricted airways.
- Frequent Infections: Recurrent colds, flu, or bronchitis.
- Fatigue: Caused by reduced oxygen levels.
- Chest Tightness: A sensation of pressure or discomfort in the chest.
Complications Linked to COPD Causes
If left untreated, COPD can lead to severe complications:
- Heart Disease: The strain on the heart caused by low oxygen levels can result in cardiovascular issues.
- Lung Infections: Chronic inflammation makes individuals more susceptible to pneumonia and bronchitis.
- Pulmonary Hypertension: Elevated pressure in the lungs' arteries due to prolonged damage.
- Mental Health Challenges: Breathing difficulties and reduced mobility often lead to anxiety and depression.
Preventing COPD: Steps to Take
Although some risk factors like genetics are unavoidable, most
COPD causes can be mitigated through lifestyle changes:
- Quit Smoking: Seek professional support or cessation programs.
- Avoid Lung Irritants: Minimize exposure to dust, fumes, and pollution with masks and proper ventilation.
- Stay Active: Regular exercise strengthens respiratory muscles and improves endurance.
- Get Vaccinated: Flu and pneumonia vaccines reduce infection risks, a common COPD trigger.
- Eat a Nutritious Diet: Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods like leafy greens and omega-3-rich fish.
Natural Remedies for Lung Health
Certain herbs and plants can aid in alleviating COPD symptoms:
- Eucalyptus: Helps clear airways and reduce inflammation.
- Peppermint: Soothes respiratory muscles and relieves congestion.
- Ginger: Its anti-inflammatory properties support lung function.
- Thyme: A traditional remedy for clearing mucus.
- Mullein: Used to alleviate respiratory inflammation.
Supplements Supporting Lung Health
Supplements can complement lifestyle changes for managing COPD effectively:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Help reduce inflammation in the lungs.
- Vitamin D: Supports immune function and reduces respiratory infections.
- N-acetylcysteine (NAC): Aids in thinning mucus and reducing oxidative stress.
- Magnesium: Relaxes bronchial muscles to ease breathing.
- Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10): Boosts energy production in lung cells.
Managing COPD with Lifestyle Adjustments
In addition to addressing
COPD causes, the following tips can enhance lung health and slow disease progression:
- Practice Breathing Techniques: Exercises like pursed-lip breathing can improve oxygen exchange.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking water helps thin mucus, making it easier to clear from the airways.
- Use a Humidifier: Reducing dryness in the air prevents irritation of the respiratory system.
- Avoid Triggers: Steer clear of smoke, strong odors, and air pollution to reduce flare-ups.
Conclusion
COPD is a challenging condition, but understanding its causes, symptoms, and prevention methods can make a world of difference. Addressing modifiable risk factors, embracing a lung-friendly lifestyle, and exploring natural remedies can empower individuals to manage symptoms effectively. By taking proactive measures, you can protect your lungs and lead a healthier, more active life.
References
- American Lung Association - Comprehensive Guide to COPD Visit the American Lung Association
- Mayo Clinic - COPD Causes and Risk Factors Visit Mayo Clinic
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) - Preventing COPD Visit NHLBI
- Understanding Lung Cancer
- How to Quit Smoking and Improve Your Health